Optical Mirrors
Feature and advantage:
- Highly Efficient Light Reflection
- Precise Light Path Control
- Broad Spectral Adaptability
- Cost-Effectiveness
PRODUCT
Detail
An optical mirror is an optical component that utilizes the principle of light reflection. By applying a coating on its surface, it enables the light to be reflected in a specific direction. It changes the propagation direction of the incident light while minimizing the absorption or scattering of light energy. The reflective surface is typically made of materials with high reflectivity, such as aluminum, silver, gold, or multilayer dielectric films. Depending on the application, it can be designed in various geometric shapes, including plane, spherical, and parabolic. It is widely used in astronomical telescopes, laser physics and spectroscopy, laser processing equipment, and optical inspection.
|
Specifications
|
|
|
Material
|
N-BK7, H-K9L, Fused Silica, etc.
|
|
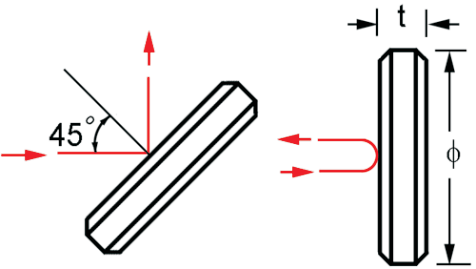
Diameter Tolerance (mm)
|
+0.0/-0.2 (General), +0.0/-0.02 (High Precision)
|
|
Thickness Tolerance (mm)
|
±0.2 (General), ±0.005 (High Precision)
|
|
Clear Aperture
|
>80% (Small Size), >95% (Large Size)
|
|
Flatness (per 25mm@633nm)
|
λ (General), λ/10 (High Precision)
|
|
Incidence Angle
|
0deg or 45deg
|
|
Surface Quality
|
60/40 (General), 10/5 (High Precision)
|
|
Parallelism
|
3 min. (General), 3 sec. (High Precision)
|
|
Coating
|
Dielectric coated HR, or metal coated Al, Ag, Au etc.
|